Climate is a measure of the average pattern of variation in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological variables in a given region over long periods of time.
Climate is different from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region.
Climate Classification:-
The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used form of the Köppen classification has five primary types labelled A through E.
These primary types are
- A, Tropical;
- B, Dry;
- C, Mild Mid-Latitude;
- D, Cold Mid-Latitude; and
- E, Polar
The five primary classifications can be further divided into secondary classifications such as rain forest, monsoon, tropical savannah, humid subtropical, humid continental, oceanic climate,Mediterranean climate, steppe, subarctic climate, tundra, polar ice cap, and desert.
Rain forests are characterized by high rainfall, with definitions setting minimum normal annual rainfall between 1,750 millimetres (69 in) and 2,000 millimetres (79 in). Mean monthly temperatures exceed 18 °C (64 °F) during all months of the year.
A monsoon is a seasonal prevailing wind which lasts for several months, ushering in a region's rainy season. Regions within North America, South America, Sub-Saharan Africa, Australia and East Asia are monsoon regimes.
A tropical savannah is a grassland biome located in semiarid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes, with average temperatures remain at or above 18 °C (64 °F) year round and rainfall between 750 millimetres (30 in) and 1,270 millimetres (50 in) a year. They are widespread on Africa, and are found in India, the northern parts of South America, Malaysia, and Australia.
The humid subtropical climate zone where winter rainfall (and sometimes snowfall) is associated with large storms that the westerlies steer from west to east. Most summer rainfall occurs during thunderstorms and from occasional tropical cyclones. Humid subtropical climates lie on the east side continents, roughly between latitudes 20° and 40° degrees away from the equator.
A humid continental climate is marked by variable weather patterns and a large seasonal temperature variance. Places with more than three months of average daily temperatures above 10 °C (50 °F) and a coldest month temperature below −3 °C (27 °F) and which do not meet the criteria for an arid or semiarid climate, are classified as continental.
An oceanic climate is typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of all the world's continents, and in south eastern Australia, and is accompanied by plentiful precipitation year round.
The Mediterranean climate regime resembles the climate of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, parts of western North America, parts of Western and South Australia, in south western South Africa and in parts of central Chile. The climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
A steppe is a dry grassland with an annual temperature range in the summer of up to 40 °C (104 °F) and during the winter down to −40 °C (−40 °F).
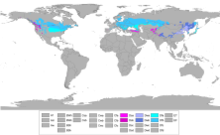
A subarctic climate has little precipitation, and monthly temperatures which are above 10 °C (50 °F) for one to three months of the year, with permafrost in large parts of the area due to the cold winters. Winters within subarctic climates usually include up to six months of temperatures averaging below 0 °C (32 °F).
Tundra occurs in the far Northern Hemisphere, north of the taiga belt, including vast areas of northern Russia and Canada.
A polar ice cap, or polar ice sheet, is a high-latitude region of a planet or moon that is covered in ice. Ice caps form because high-latitude regions receive less energy as solar radiation from the sun than equatorial regions, resulting in lower surface temperatures.
A desert is a landscape form or region that receives very little precipitation. Deserts usually have a large diurnal and seasonal temperature range, with high or low, depending on location daytime temperatures (in summer up to 45 °C or 113 °F), and low night time temperatures (in winter down to 0 °C or 32 °F) due to extremely low humidity. Many deserts are formed by rain shadows, as mountains block the path of moisture and precipitation to the desert.
Tropics:-
The tropics is a region of the Earth surrounding the Equator. It is limited in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the northern hemisphere and the Tropic of Capricorn in the southern hemisphere at 23° 26′ 16″ (or 23.4378°) S; these latitudes correspond to the axial tilt of the Earth.
The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone. The tropics include all the areas on the Earth where the Sun reaches a sub-solar point, a point directly overhead at least once during the solar year.
"Tropical" is sometimes used in a general sense for a tropical climate to mean warm to hot and moist year-round, often with the sense of lush vegetation.Many tropical areas have a dry and wet season. The wet season, rainy season or green season, is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region falls.
Tropical plants and animals are those species native to the tropics. Tropical ecosystems may consist of rainforests, dry deciduous forests, spiny forests, desert and other habitat types. There are often significant areas of biodiversity, and species endemism present, particularly in rainforests and dry deciduous forests.
Savanna Grasslands:-
A savanna or savannah is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of grasses.
No comments:
Post a Comment